You can’t miss a frog when you see one. Its unusual body makes it stand out, with its bulging eyes, webbed feet, and long tongue.
From a human point of view, frogs don’t seem to have ears. This brings a lot of questions to mind: How do frogs hear sounds? Do frogs have ears?
Frogs do hear, and that does suggest that they have a method of hearing. However, you will not see any protruding hearing organ on any frog, which means there is a difference between how we hear and how they do.
Let’s delve deeper into the unique frog ears and how they pick up sounds.
Do Frogs Have Ears?
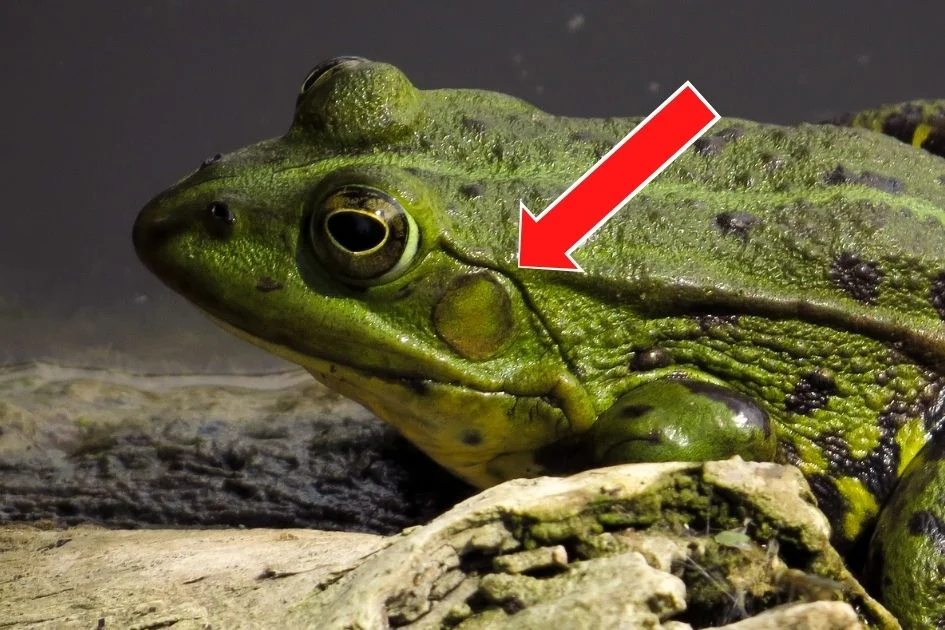

Frogs don’t have external ears like humans and other mammals like wolves, cats, and rodents. However, they do have ears.
The only difference is in the structure of their ears. Here’s what we mean:
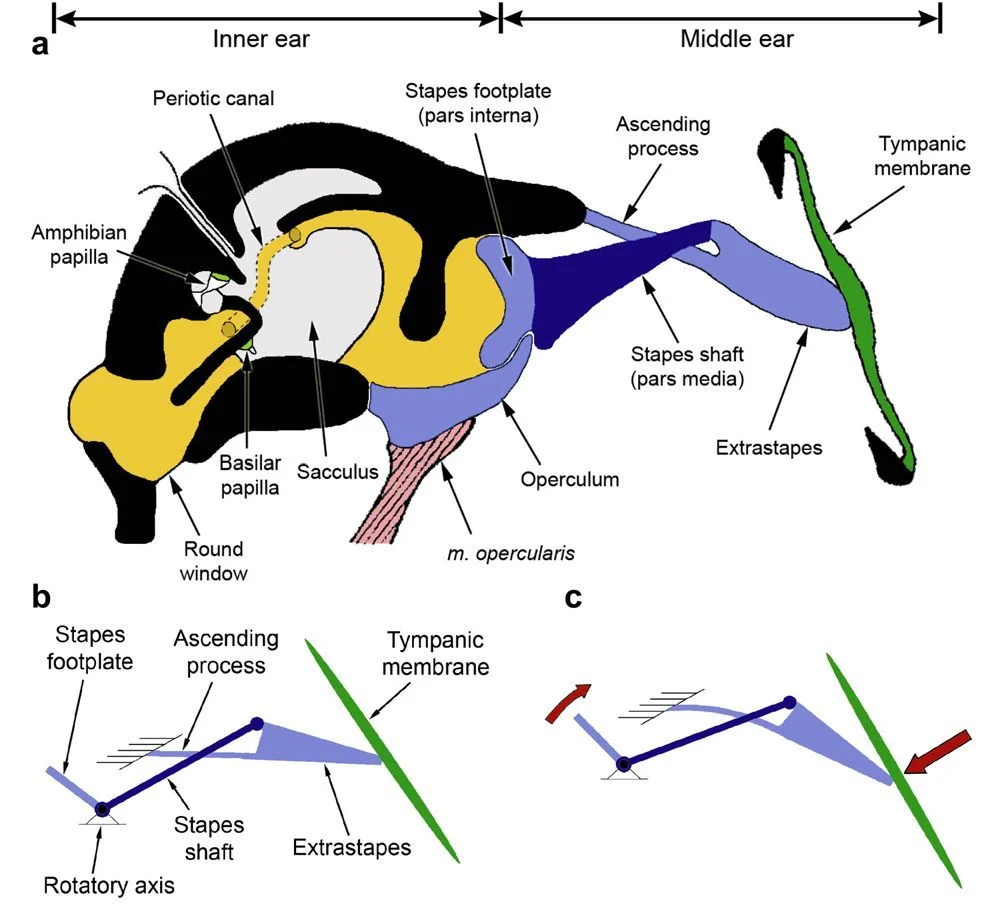
A typical animal’s ears have 3 parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
Frogs come with an inner ear and a middle ear, but do not have any outer ear. In place of the outer ear, they have a tympanum, which looks a bit like a human’s eardrum.
The tympanum is located behind the eye and has the job of transmitting sound waves to the inner ear where the waves can then be processed. It is the only external hearing structure frogs have.
Frogs aren’t the only animals without an outer ear. Other amphibians like the toad and the salamander have no outer ear. Reptiles don’t have it too.
Interestingly, not all mammals have an outer ear. The echidna and the platypus both lack outer ears, but instead of a tympanum, they have a different outer ear. Birds have a unique outer ear too.
How Do Frogs Hear Sound?
Frogs might not have a mammal’s outer ear, but it doesn’t deprive them of hearing. Even more, frogs and humans have similar hearing methods.
What is unique about frog’s ears?
The tympanum in the frog’s ears picks up sound waves and vibrates. The sound waves and vibrations go to the middle ear, which does the job of amplifying sounds before sending them to the inner ear.
The inner ear is responsible for converting the sound and vibrations into electrical signals. The destination of these signals is the frog’s brain.
The whole process happens very fast, and frogs can use the sound to protect themselves from their prey, find food or locate a potential mate.
As we saw above, there are frogs with no middle ears. These frogs use their skins, lungs, and mouth to pick up vibrations, which help them navigate their environment.
Do Frogs Have Good Hearing?

Frogs have very good hearing, better than we expect from these most intelligent amphibians.
Their hearing is even considered stronger than that of humans as they can pick up sounds at a frequency that humans can’t.
Their sight is what’s less developed. To compensate for that, they hear remarkably well.
As we explained above, frogs “hear” with more than their ears, which makes them very sensitive to their surroundings.
They can pick up predator sounds and differentiate them. They also know which croak belongs to members of their species and which doesn’t.
Do All Frogs Have Ears?
Having established that frogs have an inner and middle ear as well as a tympanum, the next question to consider is if all frogs have ears.
With so many frog species spread in different parts of our world, can we find a frog species without ears?
The answer is yes! Some frog species have no middle ears, and as such, have no ears.
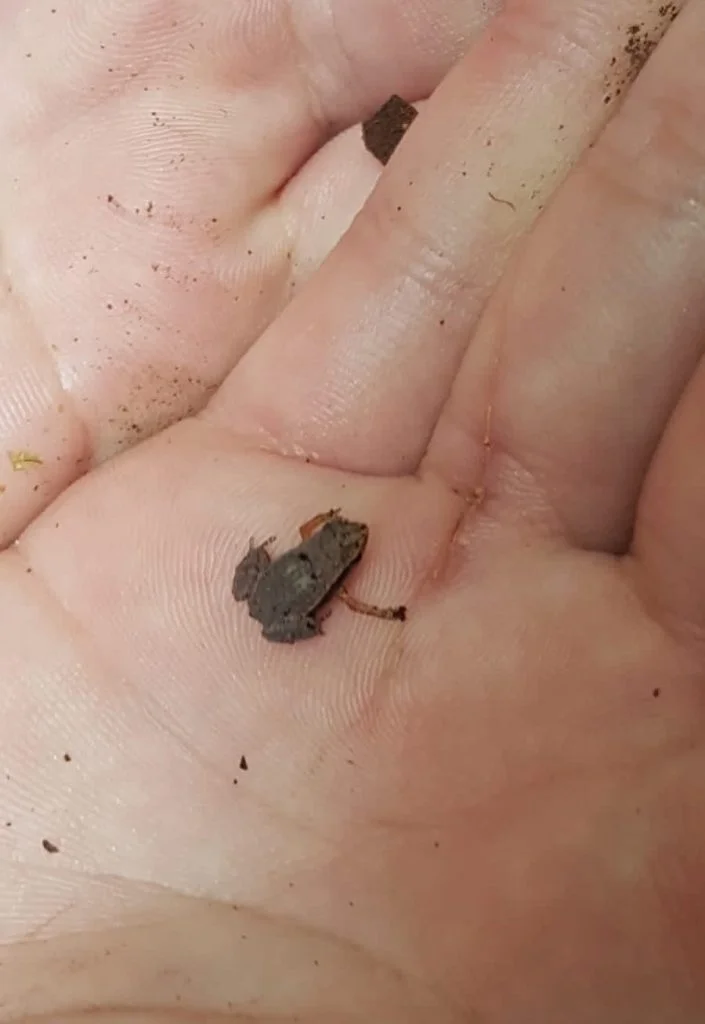

An example is the Gardiner’s Seychelles frog (Sechellophryne gardineri), one of the world’s smallest frogs with only an inner structure. To hear, it relies on vibrations and its mouth.
Summary
Frogs do not have protruding animal ears like mammals, but a lot of them have middle ears and inner ears.
In place of the outer ear, they have a tympanum that picks up the sound waves that later get converted into signals.
Not all frogs have middle ears, though. Some frogs have to rely on other parts of their body to pick up and interpret sounds.
Check out these interesting articles:




![How Long Can Frogs Go Without Food Or Water [Answered]](https://animalvivid.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/How-Long-Can-Frogs-Go-Without-Food-Or-Water-Answered.jpg.webp)

