Dolphins are highly intelligent and active marine mammals. They range in aquatic habitats worldwide.
These aquatic mammals feed mainly on fish and other large invertebrates, using their teeth to seize and break their food before swallowing. Because they are marine creatures, it’s easy to wonder do dolphins have tongues.
Dolphins have tongues on the floor of their mouths. The dolphin’s tongue is typically long, thin, and pink.
It helps them swallow, and in their offspring, it helps create negative pressure within the mouth that enables them to suckle and swallow milk from the mother.
This article will give more insights into the dolphin’s tongue, what they use it for, and other interesting facts you should know.
Do Dolphins Have Tongues?
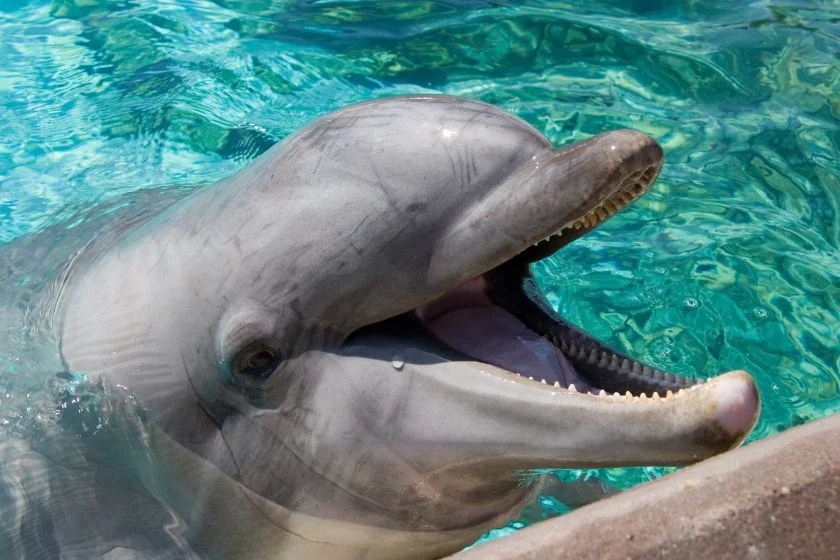

If you have wondered if dolphins have tongues like other mammals, the answer is yes, they do.
Although the size of a dolphin’s tongue is not known, it is quite long. The tongue of a dolphin is restricted in how far it can reach.
Dolphins aren’t mouth breathers and lack vocal cords, and they cannot use their tongue to communicate as distinctly as humans do. 1
What Do Dolphins Use Their Tongues For?
Aside from swallowing, the tongue is one of the dolphin’s sense organs for taste.
While it is unknown to what extent they can taste their meals, they have been observed to express preferences when given fish in marine park tanks.
What Do Calves Use Their Tongues For?
One unique feature of calves is what they use their tongue for and how they use it. When calves are suckling from their mother, they improvise their tongues as straws for suckling.
The dolphin calves attach their tongues to the nipple of the mother dolphin, and the mother releases milk to the calves through their tongues, which they use as a straw.
The quantity of milk the calves suck is controlled by the mother, not the calf. The complete feeding of a calf is done in a few seconds.
Dive Deeper: Do Dolphins Lay Eggs Or Give Birth To Their Young?
Can Dolphins Curl Their Tongues?
All dolphins can curl their tongues, and not just for the fun of it. There are tiny frills located along the edge of their tongues that connect when curled to form a watertight straw.
This straw is what a baby dolphin uses to feed. It connects the tongue straw to the mother’s mammillary slit to suckle while swimming.
The Dolphin’s Mouth and Teeth
The dolphin is very popular for its fixed smile, though it actually has no form of facial expression.
They lack the facial muscles that control facial expressions. The smile is simply a characteristic of the dolphin’s facial anatomy and is unrelated to the animal’s emotional feelings.
The dolphin’s teeth have the same shape and function. There are no separate teeth for cutting, biting, and grinding. Their teeth start to appear as they’re about three months old.
By the time they’re five, they usually have all their teeth. These teeth are permanent and non-replaceable (in the case of a lost tooth).
The dolphins’ teeth are conical, pointed, and arranged on each upper jaw and lower sidelines to catch their prey firmly and prevent it from escaping.
An interesting fact about their teeth is that it grows with age. Scientists can tell the dolphin’s age by dissecting a tooth and counting the growth rings. Each growth ring represents a year in the life of the dolphin.
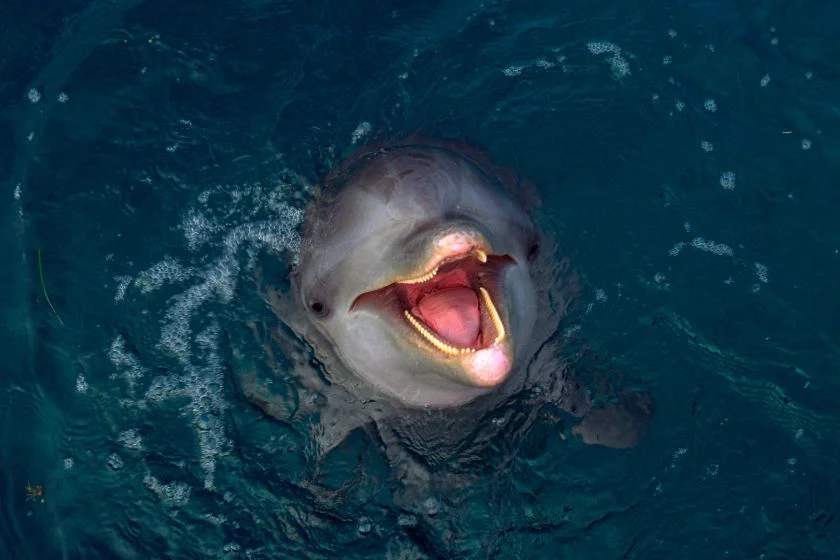

It may also use its teeth to defend or show its authority and exert dominance by raking its teeth across another dolphin’s body. Raking may leave dark scar tissue on the skin of the raked member, which later changes to white.
What Other Sense Organs Do Dolphins Have?
Apart from their tongues, dolphins possess other sense organs which serve different functions in their biological processes. They are listed below:
- Eyes: The dolphin’s eyes are specially adapted to see clearly on land and in water. They have elliptical eyes to see underwater, and with the strong muscles around them, their eyes can easily become spherical above water.
- Skin: Dolphins are very smooth mammals; their skin feels rubbery to touch and has a lot of nerve endings, thus making them very sensitive. Also, physical contact is among the ways dolphins communicate with themselves.
- Ears: Dolphins have small ear openings on both sides of their heads for hearing above the water. Their lower jaw bones help direct sounds to their middle ear when underwater.
- Blowholes (nostrils): These marine mammals have nostrils on the top of their head but can’t smell because they lack olfactory nerves.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do dolphins eat?
Dolphins are carnivores and active predators that feed on various fish, squid, and crustaceans like shrimp.
How many species of dolphins are there?
Dolphins are a unique and diverse group of over 40 species. These different species of dolphins are distributed worldwide in oceans and rivers. The two popular types of dolphins include river dolphins and ocean dolphins.
Wrap Up
Dolphins, like every other species of animals, have tongues, which serve several functions like tasting and swallowing.
Their offspring use the tongue to draw milk out from the mother’s nipples.
Apart from the tongue, dolphins also have other sense organs like eyes and skin for effective biological functioning.
Next Up:
References & Notes
- All About Bottlenose Dolphins – Senses. [online] SeaWorld Parks.





![How Long Can A Dolphin Stay Out Of Water [Answered]](https://animalvivid.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/How-Long-Can-A-Dolphin-Stay-Out-Of-Water-Answered.jpg.webp)