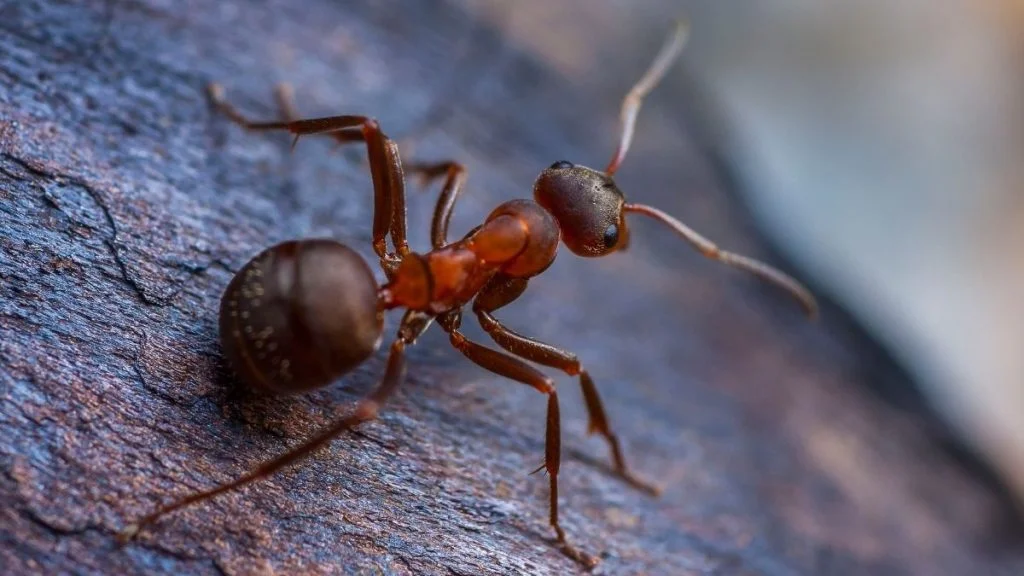
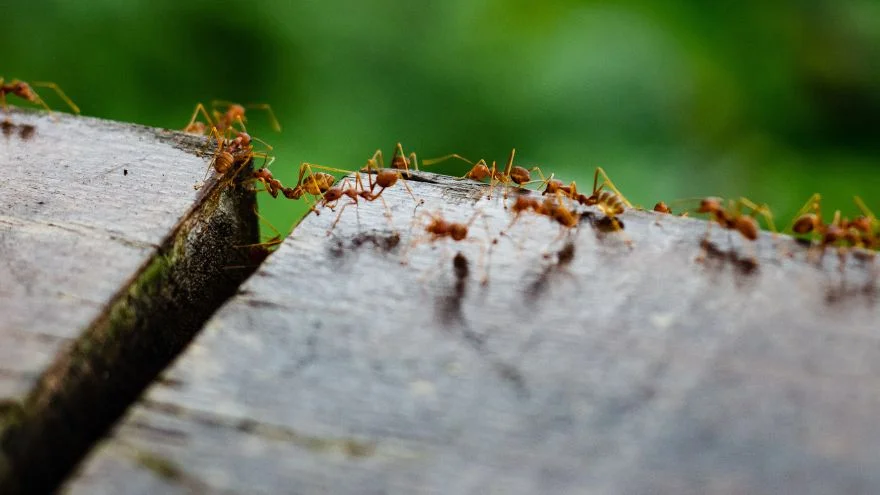
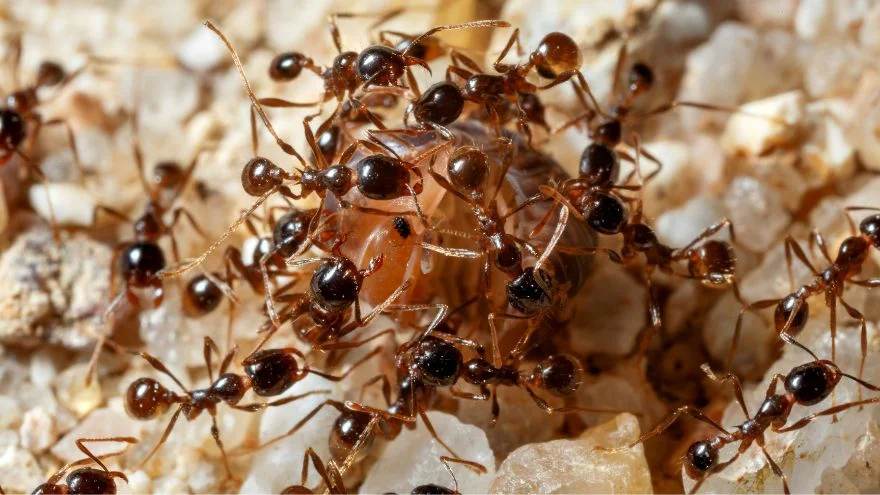
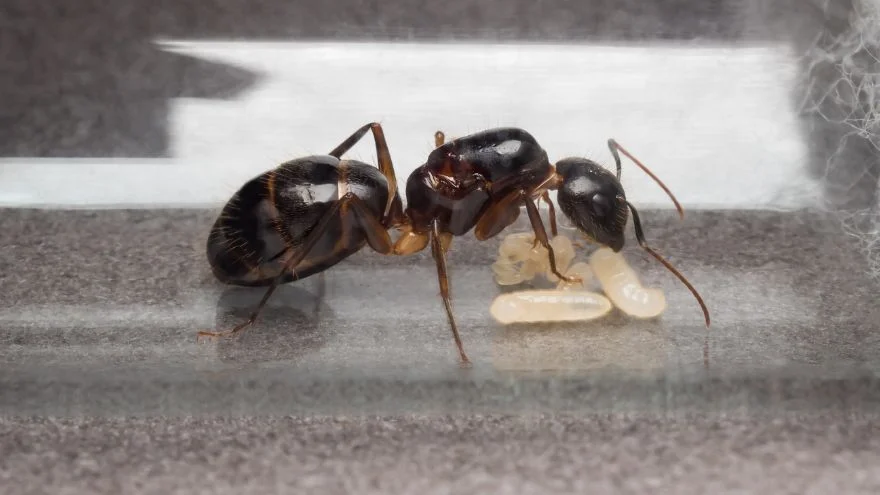
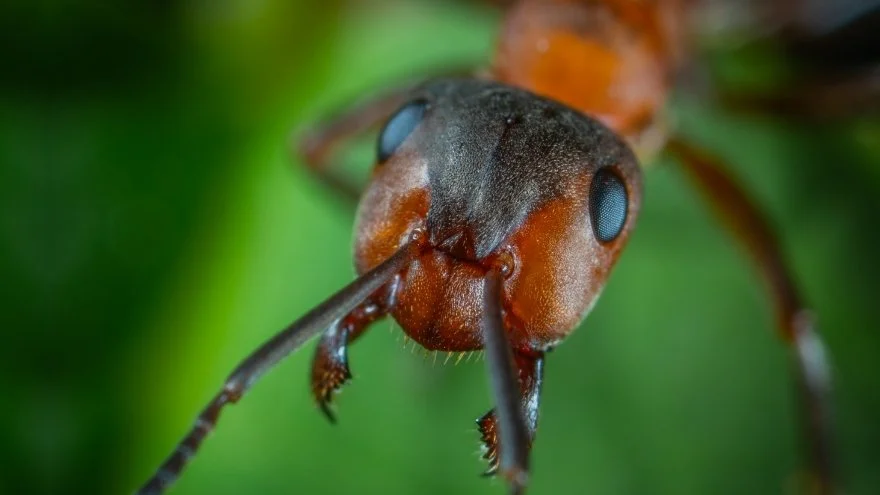
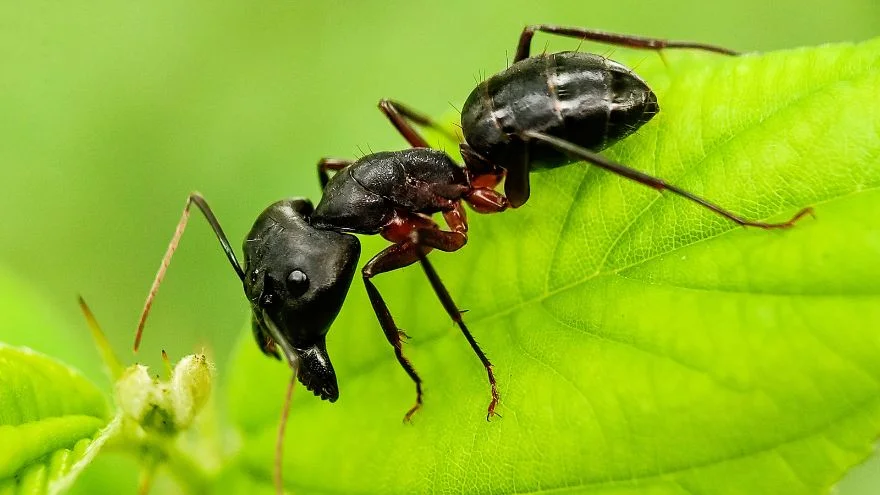
Ants are invertebrate animals from the family Formicidae that works as a colony.
They build nests by interacting and dividing labor among the individual ants that form the colony.
Staying close to a group of ants, one can quickly notice the high level of interaction and communication amongst them and might begin to wonder: Do ants have ears? Can ants hear sounds?
Ants don’t have ears, but they can hear. They can detect sound through special organs beneath their legs and sense vibrations running through the ground or wherever they stand. Hence they can warn one another of danger and hunt down prey.
If you have seen an ant, you will doubt it can hear or communicate as no ear is visible on its body like in most animals.
Read on to learn more about how ants hear and communicate effectively.
Can Ants Hear Sounds?
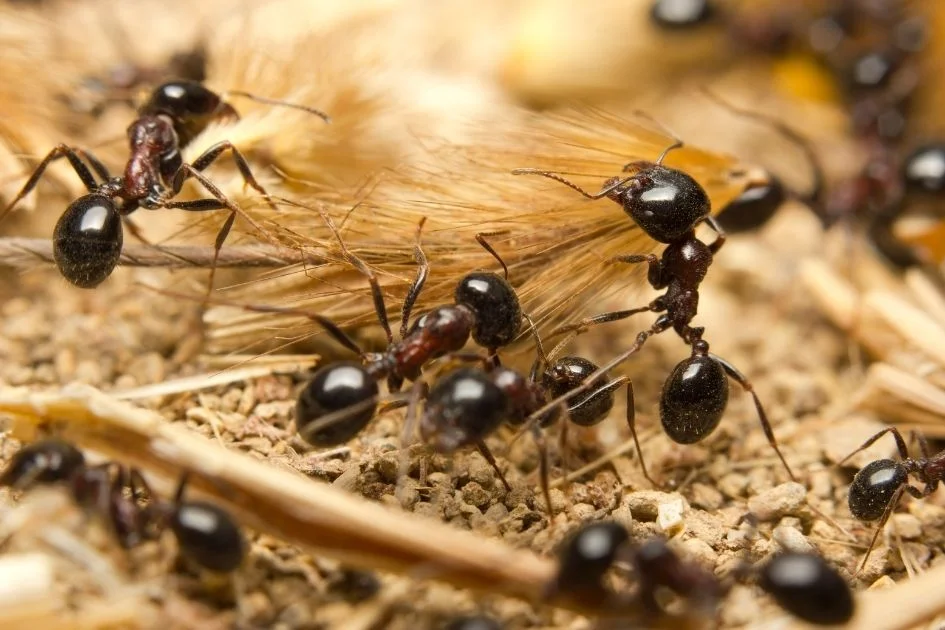

Yes, ants can hear sounds. If you define hearing only by the reception of vibrations in the form of sounds, then that will be a partial evaluation of what hearing is all about.
How ants hear is different from how humans or some other animals do. They detect vibrations and transmit different sounds to communicate different signals.
Do Ants Have Ears?
Ants are said to be social animals which keeps them at an advantage over other solitary animals.
Interactive animals like ants depend a lot on their communication while working as a group, and their similarity with other insects includes their ability to hear, touch, and smell.
Still, unlike humans and some other animals, they do not have the pronounced structural hearing of the ear.
The absence of the ear is evident as you notice that while looking at one. However, that doesn’t mean that they don’t hear nor communicate.
To humans, hearing can only be possible with the ear, but it is different in the case of ants.
They can sense and hear through other body structures, parts, and mechanisms, enabling them to send signals.
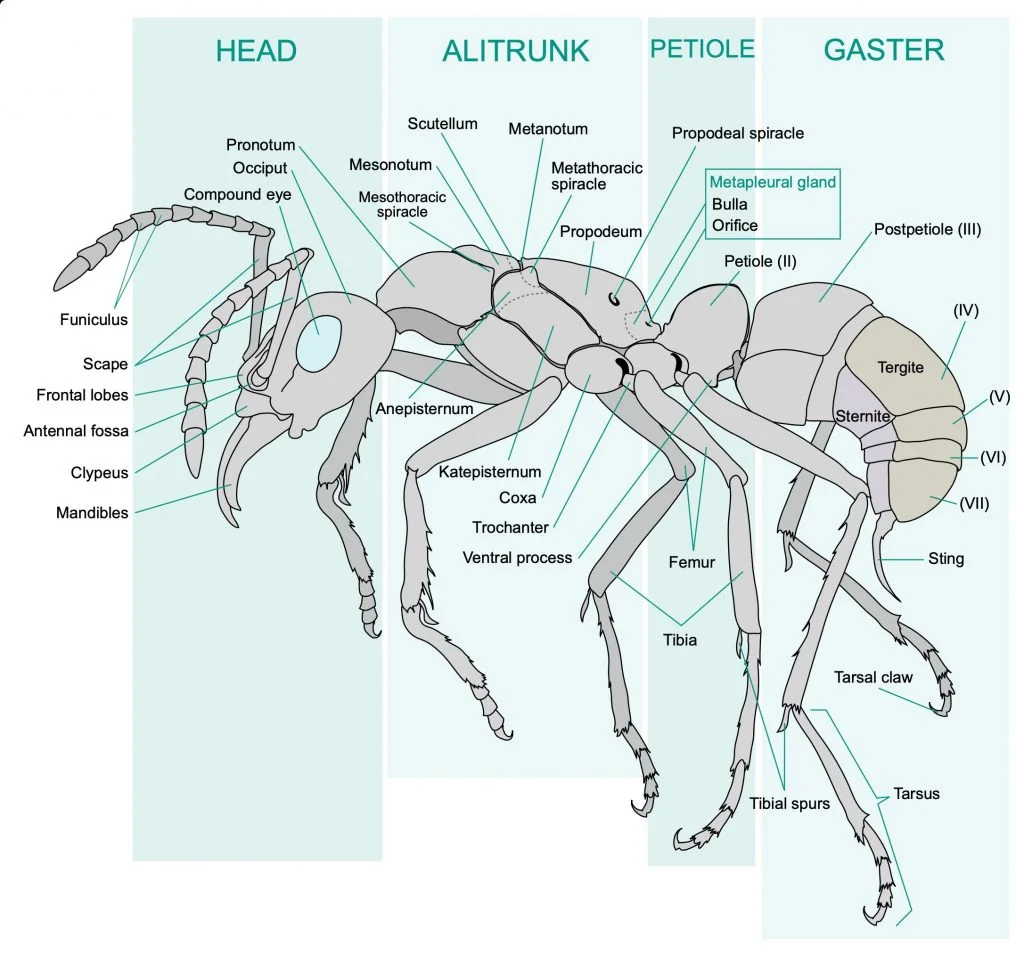
The antenna in an ant’s body helps sense vibrations and sounds; it can pick up different kinds of chemicals and feel objects while moving. It acts as the sensory organ of the ant, thus helping it detect vibration.
However, it is not the only way they hear; there are other ways the ant detect sound and communicate with one another.
How Do Ants Communicate?
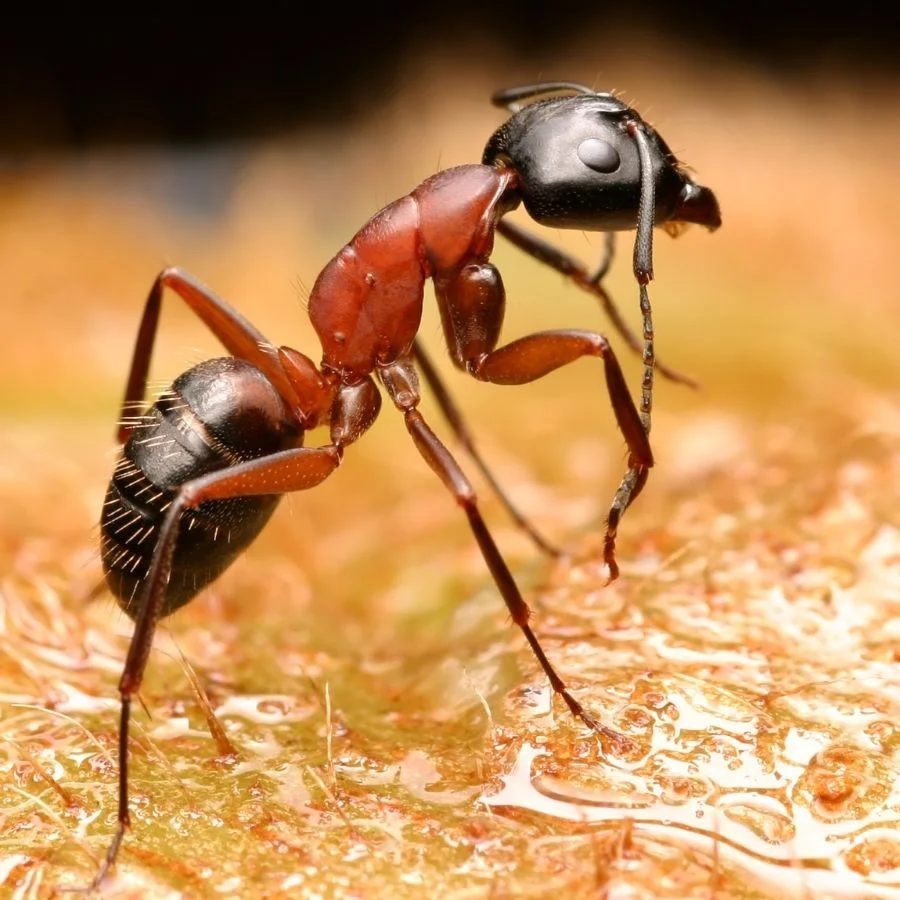

Ants can communicate with one another through the secretion of pheromones and detecting sounds.
Pheromones are chemicals used by insects and other animals to communicate; they can travel a long way, though how fast they travel depends on wind speed and direction.
They use vibrations to produce sounds through a process known as stridulation.
They perform this by kneading their mandibles and the inflated part of their abdomen located behind the ant’s pedicel, known as gaster, to produce sounds.
The sound produces ground vibration, which the other members of the colony or species detect with the aid of their subgenual organ below the ant’s femur and tibia leg joint.
Why Do Ants Communicate?
As a colony, ants communicate by sending signals; they do so for different reasons, mostly as a warning or hunting signal.
Warning
When ants perceive danger, some species send a warning signal.
They do so by beating their belly on the substrate of the ant nest, which develops an alarm that enables others to drum their abdomen, and then the worker ants get ready to defend the queen ant.
Protecting the queen is the most important job of a worker ant, as the death of the queen will lead to the colony’s death.
Hunting Signal
Most insects like ants and spiders use silken strands of vibration to sense their prey.
In most cases, the weaker insects use the vibration to detect the presence of the strong ones, and ants get involved in this hunting process.
Not all ants hunt other animals; most of them feed only on plant matters like grains and leaves. In the case of those that hunt, vibrations tell them where they might be able to find prey.
FAQs
Can ants hear better than humans?
The ant’s sense of hearing is not like that of the human being who perceives sound through the auditory canal.
Ants would rather hear sounds through vibrations and the production of chemical hormones that travels wide, so it is an illusion to say that ants hear more than humans.
Do ants have Emotions?
Ants can be said to understand and be attracted to what is pleasant and avoid the opposite, unlike humans with more complex feelings like anger, love, etc.
The sensory hairs of ants are located outside their body, making it impossible to sense damage inside. This is why parasites can quickly destroy them once they can penetrate without alerting their sensors.
Do ants have eyes?
Yes, ants have eyes, but not the same as some other animals. It has two sets of eyes: two compound eyes, and three simple eyes.
They primarily use compound eyes, which consist of hundreds of individual units called ommatidia. Each ant species has a peculiar size and shape.
Despite the number of eyes they have, they have blurry eyesight and cannot see objects from far distances. Bullet ants are said to have the best eyesight among all other species.
Conclusion
Ants have various roles they play in their colony and they possess sensory organs that help them perform their functions.
Although the ant anatomy does not indicate the presence of ears as in several other animals, ants can hear and detect sound amongst themselves.
The sounds and vibrations aid in warning and hunting purposes through the special mechanism of secretion of pheromones; they pick up vibrations with the aid of some other body parts.
Featured Image Credit: B_Zocholl / Pixabay






